Social Carbon is a national and international registered trademark with the objective of guaranteeing that projects developed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions also contribute to sustainable development using transparent and participative methods of assessment and measurement of benefits for involved parties and the environment.
The Ecologica Institute has been developing the concept of Social Carbon since the pilot carbon capture projects in the state of Tocantins, where carbon reduction and carbon sequestration resulted from projects that promoted improvements in the livelihood of local communities through the interaction the population with the project activities.
The Social Carbon Methodology (SCM)
The expression “Social Carbon” can be understood as all carbon absorbed/reduced from actions that financially benefit and improve the livelihoods of communities involved in emission reduction/climate change projects. These projects guarantee welfare and citizenship without degrading resource bases.
The Methodology has been used to analyze the reality and guide sustainable development initiatives associated with climate change.
Objectives of the Social Carbon Methodology
The main objective of the Social Carbon Methodology is to contribute to sustainable development, encouraging the enhancement of sustainability resources (which include Carbon, Biodiversity, Natural, Financial, Human and Social resources). Enhanced sustainability resources helps the community or company involved in carbon emission reduction projects achieve a sustainable process, generating carbon credits in addition to social, environmental and financial gains.
Specific Objectives
- Valuing potentials and perspectives of communities using a community vision.
- Identifying global change impacts in the local scenario and promoting the analysis of local players.
- Identifying ecosystems and biodiversity potentials, and identifying possible ecological sensitivities while promoting and valuing the use of traditional knowledge.
- Seeking social inclusion and acknowledging gender-related issues, promoting improvements in the quality of life of the less fortunate through the reduction of social inequalities.
Follow-up Mechanisms
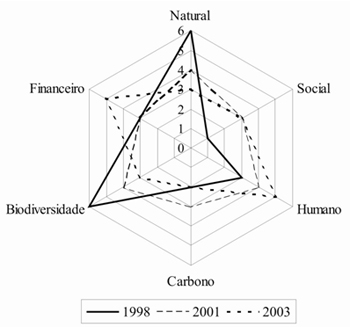
The Social Carbon Methodology represents results visually in the form of a hexagon where each vertex corresponds to a sustainability resource. The central point of the hexagon (value 0) represents zero access to resources, while the outer edge (value 6) is the maximum access. Each of the resources can display values on a scale from 0 to 6, based on the variables and defined scenarios.
The resources and indicators development evaluation over the years is carried out through annual diagnoses of project activities. As changes occur in businesses and communities activities of project surroundings, the lines move, modifying the polygon formed over time.
The methodology focuses on the effective participation of communities in all processes, making it amenable to social control. Participatory workshops, interviews and visits at the project site are used for monitoring. The figure below shows the hexagon for the Araguaia settlement community in the municipality of Caseara, in Tocantins.
Due to its flexible and holistic dynamics, the Social Carbon Methodology can be applied to different types of projects, whether related to energy efficiency, renewable energy or forestry. The six resources are:
- Social Resource: evaluates social responsibility actions, as well as relations and the integration between NGOs and associations, and their relationship with the local community.
- Human Resource: related to the analysis of professional abilities, training and work conditions, including health and safety issues of the working environment.
- Financial Resource: is the basic capital that is available for the companies, as well as the forms of investments and financial barriers to projects.
- Natural Resource: analyses the existing relationship between the company and the environment, considering impacts on natural resources, actions that contribute to environmental conservation and maintenance of environmental services.
- Carbon Resource: this refers to the type of carbon management developed, and characteristics of the carbon capture or emission reduction project.
- Biodiversity Resource: evaluates if the project is located in important conservation areas and/or areas rich in biodiversity, as well as the presence of endangered animals in the region and economically important ecosystems with strong human interference.
Related Links